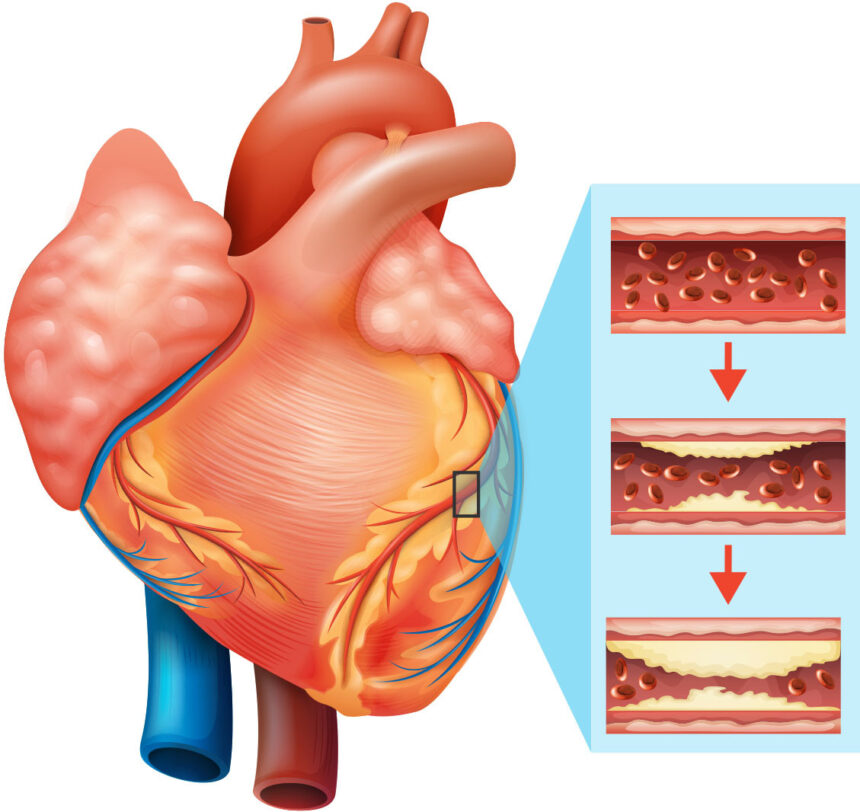
Heart diseases refer to a range of conditions that affect the heart, and they can vary in severity from mild issues to life-threatening events. Some of the most common heart diseases include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This is the most common type of heart disease. It occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque (a mixture of fat, cholesterol, and other substances). This can lead to chest pain (angina) or heart attacks.
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): A heart attack happens when a part of the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen because blood flow is blocked. It can be caused by a blockage in one of the coronary arteries, leading to damage or death of heart muscle tissue.
- Heart Failure: This condition occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to a buildup of fluid in the body (such as in the lungs or legs). It can be the result of chronic conditions like high blood pressure, heart attacks, or valve disease.
- Arrhythmias: These are irregular heartbeats. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregularly (like in atrial fibrillation). Some arrhythmias can be life-threatening if they prevent the heart from pumping blood effectively.
- Valvular Heart Disease: The heart has four valves that control blood flow through its chambers. If one or more of these valves do not function properly, it can lead to blood flow problems. This can be caused by conditions like valve degeneration, infections, or congenital defects.
- Cardiomyopathy: This refers to diseases of the heart muscle itself, where the heart becomes enlarged, thickened, or rigid, making it harder for the heart to pump blood. It can be caused by genetics, high blood pressure, or previous heart attacks.
- Congenital Heart Disease: These are heart defects present at birth. They can affect the heart’s structure, such as holes in the heart or malformations of the heart valves or blood vessels.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): While technically not a heart disease itself, PAD is closely related. It involves narrowing of the blood vessels outside the heart, especially in the legs, and can increase the risk of heart disease.
Risk Factors:
Some common risk factors for heart disease include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity or being overweight
- Lack of physical activity
- Family history of heart disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Poor diet, particularly one high in fats, salt, and sugars
- Chronic stress
Symptoms:
Symptoms of heart disease can vary depending on the condition but might include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Irregular heartbeats
- Pain or discomfort in the upper body (arms, neck, jaw, back, or stomach)
Prevention:
While some factors like genetics can’t be controlled, many forms of heart disease can be prevented or managed by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including:
- Eating a balanced, heart-healthy diet (low in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium)
- Exercising regularly
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Not smoking
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Managing stress
- Regular health check-ups to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels
Treatment:
Treatment for heart diseases varies depending on the specific condition, but it may include:
- Medications (e.g., for blood pressure, cholesterol, or blood thinners)
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, stress management)
- Surgery (e.g., angioplasty, bypass surgery, heart valve surgery)
- Implantable devices (e.g., pacemakers for arrhythmias)
- Cardiac rehabilitation programs
It’s important to recognize the symptoms of heart disease early and seek medical advice if you have concerns about your heart health.